
The battle of the bulge is a losing proposition for many Americans. According to data derived from the most recent (2015–2016) National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), the prevalence of obesity among U.S. adults was 39.8%.(1)
Visceral fat—the deeper belly fat that accumulates around the organs of the abdominal cavity, is linked to many health disorders that include heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure (hypertension, and dementia.
With the evidence mounting on the associations between obesity, heart disease (CVD), and type 2 diabetes (T2D), to an increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease, an increased awareness of these associations and how it is all connected, now appears regularly in many popular news feeds. (more…)

The region of the brain that is most severely affected in Alzheimer’s disease is the hippocampus.
The hippocampus and adjacent structures (hippocampal formation) in the medial temporal lobe of the brain is responsible for turning information we gather from our experiences and environment into memory and learning retention that can be retrieved from the neural networks they are wired into.
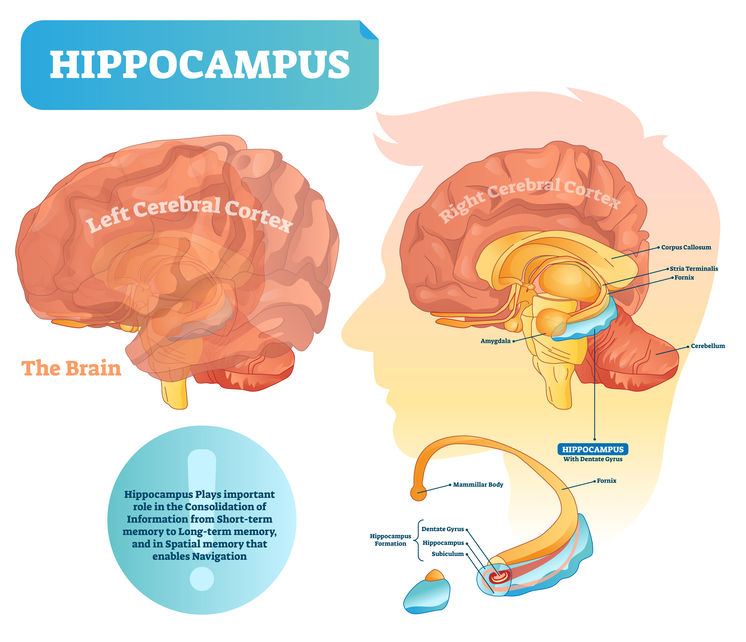
As the hippocampus shrinks from the disease processes associated with Alzheimer’s disease, the ability to make new memories vital to everyday tasks are lost. Information processing and memory retention in the hippocampus is dependent on new brain cells (neurons) growing and establishing new connections.
Recent research now reveals that exposures to lead can alter the normal development of newly born neurons (neurogenesis) in this part of the brain vital to learning and memory formation. For more on neurogenesis, please read my article: “Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor—Growth Factors in Neurogenesis and the Protection Against Alzheimer’s Disease Progression“. (1) (more…)









