In a recently published study—NutriNet-Santé (10/2018)—that included the analysis of dietary records of 84,158 French adults that spanned between May 2009 and June 20017— the study authors concluded found that “Higher intakes of polyphenols, especially anthocyanins and catechins (flavan-3-ols), were associated with a statistically significant decreased cardiovascular disease risk.”(1).
The polyphenol intake was primarily derived from coffee (49%), tea (23%), fruits (17%), vegetables (8%), and wine (5%). (more…)

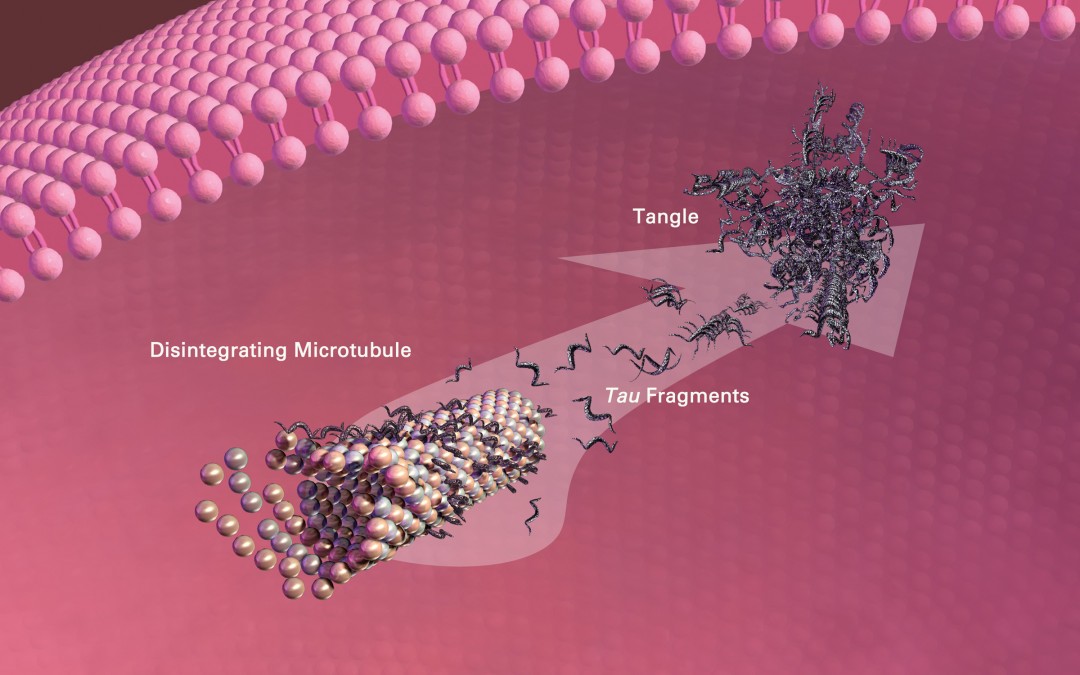
While there is active research for more effective disease-modifying drugs* the lack of any significant breakthroughs in the treatment of the Alzheimer’s disease has propelled a paradigm shift away from focusing solely on a drug solution, to an inclusive prevention model that emphasizes risk reduction and prevention, which promises to attenuate the portentous global burden incurred by the disease.
Current prevalence estimates (2016) for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) in the United States (U.S.) is approximately 5.1 million.(1) By 2050 the projected prevalence of LOAD is expected to escalate to 13.8 million and a staggering 106.8 million worldwide.(2,3) Pharmacological treatments for LOAD such as cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptor antagonists may slow its progression or attenuate specific molecular pathomechanisms associated with the disease process, but are not long term solutions or curative.
(more…)
The role of chronic inflammation in degenerative diseases associated with aging is considered to be a primary vector for the progression of neurodegenerative disorders and a powerful factor that underlies their etiology.
One needs only to look at the leading causes of mortality—heart disease and stroke, and the research models of inflammation that clearly link the pathogenesis of these disease processes in aging individuals to understand that inflammation and chronic degenerative disease are inseparable.
Since inflammation is central to aging-associated disease processes, it has been heavily investigated in models of neurodegeneration. In Alzheimer’s disease, several studies have sought to clarify whether inflammation is a causative stimulus, or a concomitant feature of the disease process. (more…)